When you hear console, what is the first thing that comes to mind??
console.log('Am here to help!!');
Yes, most of us know only about console.log when debugging a code in JavaScript. There are several ways to debug a JavaScript code like pressing f12 and putting a breakpoint in the browser, refreshing the page, and debugging happily.
Another way is using the console. By the way, do you know what a console is?
Console
Console is a command-line interface in your browser that executes snippets of code. Let's start with different types of consoles.
Console.log()
This outputs a message to the web console. It may be a single string or objects.
let output = 100
console.log(output)
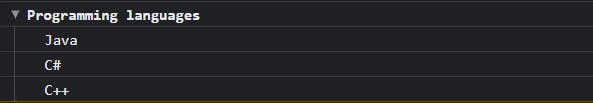
Console.group()
It creates a group of logs or messages. You can group many log statements with the console.group() and end the same group, use console.groupEnd().
console.group("Programming languages")
console.log("Java")
console.log("C#")
console.log("C++")
console.groupEnd()
Console.groupCollapsed(): This helps to structure your group of messages with a collapse feature. It is represented with a small icon that you can expand to open the logs.
Console.error()
This method writes error messages to the console.
const element = document.getElementById("id");
if (element == null) {
console.error("Error!! Element doesn't exist.");
}

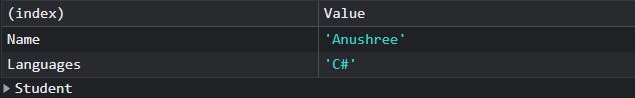
Console.table()
As the name suggests, it writes a table to the console. Pass a table object and write it to the console. The table can be sorted by clicking on the column title.
function Student(Name, Languages) {
this.Name = Name;
this.Languages = Languages;
}
const student = new Student("Anushree", "C#");
console.table(student);
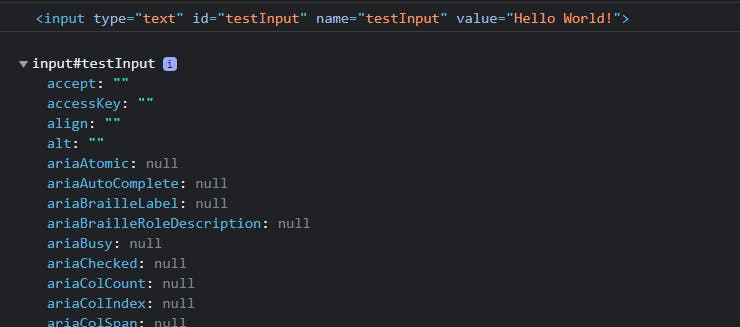
Console.dir()
It displays the list of properties of a JavaScript object. But you might be thinking console.log() can do the same thing. Will explain to you with an example..
<input type="text" id="input" name="input" value="Hashnode!!">
<script>
let inputObj = document.getElementById('input');
console.log(inputObj);
console.dir(inputObj);
</script>
Console.assert()
It displays the message when an assertion is false. When an assertion is true, nothing happens.
let first = 5;
let second = 5;
const result = "not true"
console.assert(first + second == 11, first + second);

It can also help in validating JavaScript elements.
console.assert(document.getElementById("id"), "You have no element with ID 'id'");

